Tag: anchor
 Wikipedia says: An anchor is a device, normally made of metal, used to secure a vessel to the bed of a body of water to prevent the craft from drifting due to wind or current. The word derives from Latin ancora, which itself comes from the Greek ἄγκυρα (ankȳra).
Wikipedia says: An anchor is a device, normally made of metal, used to secure a vessel to the bed of a body of water to prevent the craft from drifting due to wind or current. The word derives from Latin ancora, which itself comes from the Greek ἄγκυρα (ankȳra).
Anchors can either be temporary or permanent. Permanent anchors are used in the creation of a mooring, and are rarely moved; a specialist service is normally needed to move or maintain them. Vessels carry one or more temporary anchors, which may be of different designs and weights.
Anchors achieve holding power either by “hooking” into the seabed, or mass, or a combination of the two. Permanent moorings use large masses (commonly a block or slab of concrete) resting on the seabed. Semi-permanent mooring anchors (such as mushroom anchors) and large ship’s anchors derive a significant portion of their holding power from their mass, while also hooking or embedding in the bottom. Modern anchors for smaller vessels have metal flukes which hook on to rocks on the bottom or bury themselves in soft seabed.
The vessel is attached to the anchor by the rode (also called a cable or a warp) It can be made of rope, chain or a combination of rope and chain. The ratio of the length of rode to the water depth is known as the scope.
The earliest anchors were probably rocks, and many rock anchors have been found dating from at least the Bronze Age. Pre-European Maori waka (canoes) used one or more hollowed stones, tied with flax ropes, as anchors. Many modern moorings still rely on a large rock as the primary element of their design. However, using pure mass to resist the forces of a storm only works well as a permanent mooring; a large enough rock would be nearly impossible to move to a new location.
The ancient Greeks used baskets of stones, large sacks filled with sand, and wooden logs filled with lead. According to Apollonius Rhodius and Stephen of Byzantium, anchors were formed of stone, and Athenaeus states that they were also sometimes made of wood. Such anchors held the vessel merely by their weight and by their friction along the bottom.
Fluked anchors
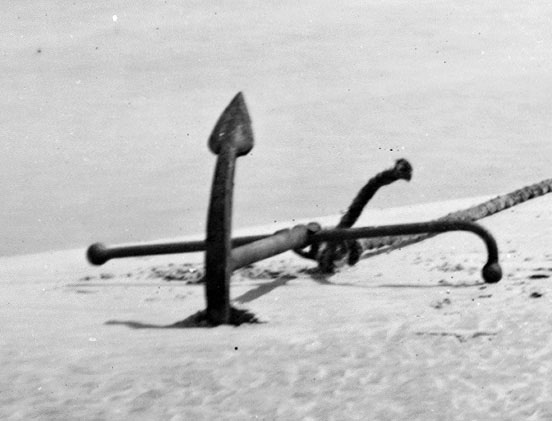
Iron was afterwards introduced for the construction of anchors, and an improvement was made by forming them with teeth, or “flukes”, to fasten themselves into the bottom. This is the iconic anchor shape most familiar to non-sailors.
This form has been used since antiquity. The Roman Nemi ships of the 1st century AD used this form. The Viking Ladby ship (probably 10th century) used a fluked anchor of this type, made entirely of iron.
Admiralty anchor
The Admiralty Pattern anchor, or simply “Admiralty”, also known as a “Fisherman”, consists of a central shank with a ring or shackle for attaching the rode (the rope, chain, or cable connecting the ship and the anchor). At the other end of the shank there are two arms, carrying the flukes, while the stock is mounted to the shackle end, at ninety degrees to the arms. When the anchor lands on the bottom, it will generally fall over with the arms parallel to the seabed. As a strain comes onto the rode, the stock will dig into the bottom, canting the anchor until one of the flukes catches and digs into the bottom.
The Admiralty Anchor is an entirely independent reinvention of a classical design, as seen in one of the Nemi ship anchors. This basic design remained unchanged for centuries, with the most significant changes being to the overall proportions, and a move from stocks made of wood to iron stocks in the late 1830s and early 1840s.
Since one fluke always protrudes up from the set anchor, there is a great tendency of the rode to foul the anchor as the vessel swings due to wind or current shifts. When this happens, the anchor may be pulled out of the bottom, and in some cases may need to be hauled up to be re-set. In the mid-19th century, numerous modifications were attempted to alleviate these problems, as well as improve holding power, including one-armed mooring anchors. The most successful of these patent anchors, the Trotman Anchor, introduced a pivot at the centre of the crown where the arms join the shank, allowing the “idle” upper arm to fold against the shank. When deployed the lower arm may fold against the shank tilting the tip of the fluke upwards, so each fluke has a tripping palm at its base, to hook on the bottom as the folded arm drags along the seabed, which unfolds the downward oriented arm until the tip of the fluke can engage the bottom.
Handling and storage of these anchors requires special equipment and procedures. Once the anchor is hauled up to the hawsepipe, the ring end is hoisted up to the end of a timber projecting from the bow known as the cathead. The crown of the anchor is then hauled up with a heavy tackle until one fluke can be hooked over the rail. This is known as “catting and fishing” the anchor. Before dropping the anchor, the fishing process is reversed, and the anchor is dropped from the end of the cathead.
Stockless anchor
The stockless anchor, patented in England in 1821, represented the first significant departure in anchor design in centuries. Though their holding-power-to-weight ratio is significantly lower than admiralty pattern anchors, their ease of handling and stowage aboard large ships led to almost universal adoption. In contrast to the elaborate stowage procedures for earlier anchors, stockless anchors are simply hauled up until they rest with the shank inside the hawsepipes, and the flukes against the hull (or inside a recess in the hull).
While there are numerous variations, stockless anchors consist of a set of heavy flukes connected by a pivot or ball and socket joint to a shank. Cast into the crown of the anchor is a set of tripping palms, projections that drag on the bottom, forcing the main flukes to dig in.